Formation of gallstones in the gallbladder-small storage organ of the liver where bile is collected and released through mineral deposits developed into hard stone-like formations inside its cavity. Gallstones are found mostly in two sizes: as little as barley grains and some as large as golf balls. Most gallstones are bile or cholesterol stones; the pigment stones are calcium deposits. In this article, we will look at gallstones causes, types, signs & prevention.
Some will form a bigger gallstone, some will form a few smaller, mixture of both will take place; they arise from the imbalance or disturbance in one or other constituents of bile and create crystallization into Cholelithiasis.
Most of the time, they are asymptomatic or not really noticed by the patient. Such gallstones are said to be silent gallstones. But if ever it happens to be someone with a gallstone blockage, the patient will complain of pain, nausea, and extreme digestive problems.
Gallbladder: Location and Special Features
The gallbladder is a small pouch hanging under the liver, roughly pear-shaped. The gall bladder regulates the storage and discharge of bile: a greenish-yellow liquid made in the liver to aid digestion at certain times, especially after ingestion of fat. The inactive bile is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder until it is time for digestion.

Product- In fatty meals, the bile released by the gallbladder acts on said fat by breaking it into smaller units for absorption by the body.
Most of the time, gallstones are asymptomatic. However, whenever the gallstone occludes any biliary duct, one might experience excruciating abdominal pain, especially in the right upper quadrant. It is commonly called a ”gallbladder attack” or ”biliary colic.”
Gallstones in India
There are multiple studies demonstrating that different parts of the world have different pre-tendencies for that specific condition due to some unexplained or not totally understood dietary habits, lifestyle, and genetics. In India, 4% of people have gallstones, compared with 10% in the Western countries.
In fact, most individuals do not realize they may have gallstones unless they undergo an ultrasound (USG) or some other medical investigation for other health reasons.
Why Are Gallstones Set to Take an Upsurge in India?
Gallstones are more on the rise in India due to:
- The high-fat diet in the West and processed food.
- Avoiding better health care, and the ease of access to medical tests like USG.
- Changing lifestyles that include less physical activity and changing eating habits owing to economic factors.
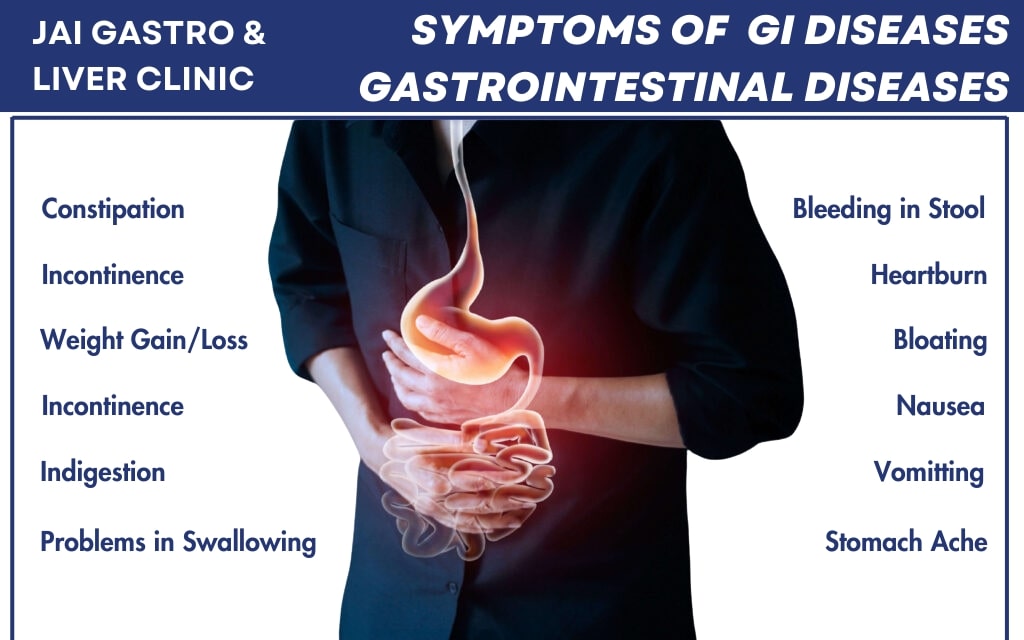
Gallstones Symptoms
Most gallstones will remain symptomless. When a bile duct is blocked due to larger stones, observed symptoms are the following:

- Severe pain in the right upper abdomen.
- This pain can last intermittently from weeks to even years.
- Nausea and vomiting may surge when eating fatty foods.
- Pain may continue for about 2 to 4 hours or longer.
- A fever may follow if the duration of the pain persists.
- Tenderness may be experienced in the liver area upon palpating.
- Pain radiating to the back, right shoulder, or chest.
- Loss of appetite or the rare and severe possibility of unexplained weight loss.
- Jaundice will set in (yellow discoloration of skin and sclera).
- In rare cases, frightening manifestations such as severe vomiting of blood.
- These aforementioned symptoms are usually common to both genders.
Classification of Gallstones
Gallstones are primarily classified into two classes:
Cholesterol Gallstones
Cholesterol gallstones are made up predominantly of cholesterol, and therefore the most common.
They occur when the stones in the gallbladder contain more than half of their weight as cholesterol.
Mixed Gallstones
Mixed gallstones contain cholesterol between 20 and 50% along with another material (mostly pigment stones).
Pigment Gallstones
Pigment stones are mainly made of calcium bilirubin formed by the breakdown of red blood cells. Pigment stones contain less than 20% of cholesterol; the main component is bile pigment.
In the Western world, cholesterol stones are the most predominant, while in Asia, about seven of the gallstones are pigment stones.
There are two forms of pigment stones – mainly black and brown pigment stones.
Black Pigment Gallstones
Black pigment gallstones occur due to blood-borne disorders, like liver diseases or sickle cell problems.
Brown Pigment Gallstones
Brown pigment gallstones occur due to infections in the bile duct by parasites or bacteria.
People More Prone to Gallstones
Stones develop in predisposed conditions namely age: fall into the bracket of above 40 years:
- Gender: hormonal changes through pregnancy and birth control pills cause gallstones in women more likely than men.
- Overweight: Exceedingly, excess weight cholesterol tends to cause gallstones.
- Crash dieting: loss in weight tends to tilt the bile balance.
- Bad eating habits: excessive fat, processed foods, or more sugar intake is another risk for gallstones development.
- Lack of Exercise: This one will very greatly favor gallstone formation.
- Chronic illness: Diabetes and high sugar level increases the risk of gallstones.
Gallstones Complications
Untreated gallstones may lead to very serious complications like:

- Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder with agonizing suffering.
- Jaundice: Yellowish staining of the skin and eyes owing to blockage in pathways of bile.
- Cholangitis: infection of bile ducts which might probably become life-taking. It may be one of the manifests of your gallstones.
- Gallstone ileus: A complication whereby movement stone blocks the intestines leading to constipation.
- Bouveret’s syndrome: It is a condition where large gallstones reach the duodenal bulb, blocking the intestines.
- Pancreatitis: It is inflammation of the pancreas one would have with gallstone obstruction of ducts.
- Gallbladder Cancer: It is also known as GBC. Occurs when large gallstones or polyps are untreated.
Gallstones Prevention, Diagnosis & Treatment
Following are the ways you can prevent gallstones from forming.
Preventing Gallstones from Forming
- It is suggested to have a diet rich in fiber, consisting of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Avoid consuming fatty and refined foods full of sugar.
- Get proper exercise, which will keep your weight healthy.
- Drink a lot of water to help the bile move freely through the duct.
- Reduce or slow down any weight fall.
Diagnosing Gallstones
Following are the methods or procedures for diagnosing gallstones.
- Physical Examination: Palpation can be done for tenderness in the abdomen.
- Liver Function Test: to monitor any type of problems relating to bile.
- Imaging Tests: CT Scan and MRI Scan can show detailed images of the body, capturing gallstones as well.
- Blood Test: A general blood test can tell a lot. The practitioner can easily indentify signs of jaundice, pancreatitis, or any other infection.
- Ultrasound (USG): This is the best and utmost test for gallstones.
Gallstones Treatment
Following are the methods or procedures to treat gallstones.
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A remote method for gallbladder excision.
- Open Cholecystectomy: an elaborate procedure done on patients with greater severity.
- ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography): The name given to a procedure where gallstones are dislodged from the bile duct without any surgery.
- Oral Medications: Occasionally, gallstones are dissolved with medications, which may take years.
The Etiology of Gallstones
Gallstones are probably hard deposits forming from defects in bile composition occurring mainly generally in the gallbladder. Gallstones may present themselves as multiple small stones or a solitary large stone. Some persons may have gallstones that do not give rise to symptoms; Other times, the gallstones may be blocking the regular bile flowing from the gallbladder, and might cause severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and indigestion. There are many ways to possibly distinguish between these gallstones without the doctor telling you.
Gallstones Causes
Gallstones are usually composed of hardened deposits formed by little lumps, arising inside the gall bladder due to imbalance.

Increased Cholesterol in Bile
Bile-digesting fats are produced in the liver. Bile consists of cholesterol, bile salts, and one or more other materials. In most cases, all cholesterol cannot be dissolved in bile owing to excess cholesterol in the liver production, leading to crystallization and finally the slow formation of stones in the gallbladder.
Excess Bilirubin
Disintegration of red blood cells produces bilirubin. Some liver diseases, infections, and certain blood disorders increase the production of bilirubin too much in the body. Increased bilirubin levels are important in the formation of gallstones.
Poor Function of Gallbladder
Normally, the gallbladder is supposed to contract adequately and pour down the bile into the small intestine. Without this, there will be continuous accumulation and concentration of bile on the inside. This accumulates over time leading to gallstone formation.
Rapid Weight Loss
Losing weight too fast can cause gallstones. Consult your doctor if you are dropping weight quickly. The job of the gallbladder is to squuze out bile into small intestine. If this process doesn’t happen, over time it can build bile inside which can then turn into gallstones.
Extended Fasting
Extended fasting reduces gallbladder movement, causing the bile to build up. This built up bile can then turn into cholesterol, which might convert into cholesterol gallstones.
Diabetes
People with diabetes or high sugar levels often have high levels of fatty acids that are also called as triglycerides. Increased triglycerides often increase the risk for gallstones.
Risk Factors of Gallstones?
Other several risk factors are likely to expose one to the development of gallstones. Waiving all those conditions is biological while others are centered on an unhealthy lifestyle.

Increased Cholesterol in Bile
Bile-digesting fats are produced in the liver. Bile consists of cholesterol, bile salts, and one or more other materials. In most cases, all cholesterol cannot be dissolved in bile owing to excess cholesterol in the liver production, leading to crystallization and finally the slow formation of stones in the gallbladder.
Age
The older a person is, the more likely he/she is to develop gallstones. Cholesterol metabolism suffers changes with advancing age and thus favors an increased risk for stone formation.
Gender
It is the hormonal changes that elevate the risk for gallstones in women. More cholesterol in bile is promoted by increases in female hormones thus favoring stone formation. Pregnancy and oral contraceptives increase this further.
Lipid Disorders
Hypercholesterolemia raises the risk for gallstones. These conditions allow the formation of gallstones over time.
Diet
Diet plays an important role in gallstone formation. Some foods raise the risk of stone formation, while others act like preventives.
Foods That Increase Risk
- Fatty foods (fried items-red meat-butter-and-cheese).
- Processed foods (fast food, chips, sweets).
- Low-fiber diet (lack of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains).
- Excess sugar (especially from sweetened beverages and processed carbs).
Foods That Help Prevent Gallstones
- Nuts (almonds, walnuts, cashews).
- Fruits and vegetables (high in fiber and antioxidants).
- Fish oil (reducing cholesterol levels in bile).
- Whole grains (brown rice, oats, quinoa).
Obesity and Weight Loss
- Obese persons are especially at risk for gallstones-immediate risk applying mostly to females.
- Gallstone formation can occur when quick weight loss (upwards of 1.5 kg each week) occurs.
- Yo-yo dieting accelerates the risk.
Sedentary Lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle contributes to marbling/gallstone formation. Exercise for thirty minutes or more, on a daily basis lowers these risks due to improved flow of bile and metabolism
Health Problems
Diabetes and insulin resistance are how bile duct problems and gallstones are increased. It is part of liver diseases like hepatitis C and cirrhosis that forms gallstones. It Has been associated with the formation of black pigment stones and Crohn’s disease (an inflammatory bowel condition).
Alcohol & Smoking
Heavy drinking damages the liver and thus increases the risk of gallstones indirectly. Smoking is positively correlated to lamentable increased rates of gallstone formation
Gallstones Treatment Options & Medications
Treatment should be directed at gallstones causing symptoms or complications.
Surgical Options
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: It is a type of abdominal surgery used to treat gallstones in the gallbladder.
- Open Cholecystectomy: The traditional approach, for complicated cases.
Medication
- ERCP– This skilful technique removes stones from the bile duct.
- Oral bile acids– This will dissolve cholesterol stones, but the treatment will take years.
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy- Very rarely an option, it essentially uses sound to break the gallstones.
Conclusion - Gallstones Causes, Types, Signs & Prevention
patients with poor diets. Normally, they would remain asymptomatic, and if they do manifest, symptoms would entail pain, jaundice, nausea, and digestive troubles.
Prevention of gallstones warrants a healthy diet, regular exercise, and moderation in weight application. Thus, any unnecessary conditions will therefore force an easy way out through surgery.